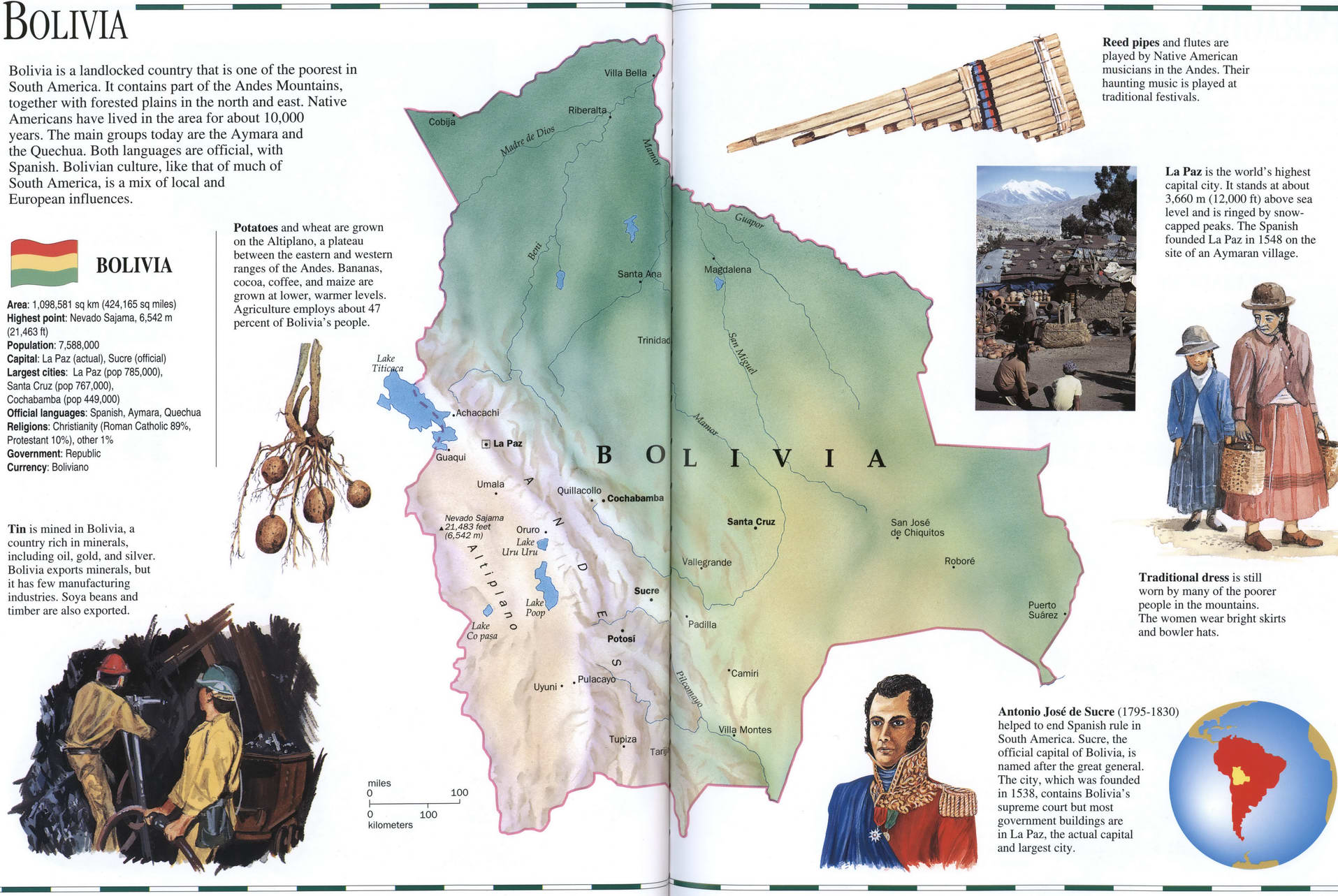
Bolivia detailed geographic map. Map of Bolivia with a brief geographical description. Bolivia on the world map.
Map of Bolivia with a brief geographical description. Bolivia on the world map.
Map of Bolivia. A more detailed map of Bolivia with the terrain and detailed information about the state with facts and figures.
Bolivia geographic description
Bolivia is a landlocked country that is one of the poorest in South America. It contains part of the Andes Mountains, together with forested plains in the north and east. Native Americans have lived in the area for about 10.000 years. The main groups today are the Aymara and the Quechua. Both languages are official, with Spanish. Bolivian culture, like that of much of South America, is a mix of local and European influences.
Bolivia highlights
Area: 1,098,581 sq km (424,165 sq miles) Highest point: Nevado Sajama. 6,542 m (21.463 ft)
Population: 7,588,000
Capital: La Paz (actual). Suae (official)
Largest cities La Paz (pop 785,000).
Santa Cruz (pop 767.000).
Cochabamba (pop 449,000)
Official languages: Spanish, Aymara. Quechua
Religions: Christianity (Roman Catholic 89%. Protestant 10%), other 1%
Government: Republic
Currency: Boliviano
Tin is mined in Bolivia, a country rich in minerals, including oil. gold, and silver. Bolivia exports minerals, but it has few manufacturing industries. Soya beans and timber are also exported.
Potatoes and wheat are grown on the Alliplano. a plateau between the eastern and western ranges of the Andes. Bananas, cocoa, coffee, and maize are grown at lower, warmer levels. Agriculture employs about 47 percent of Bolivia's people.
Reed pipes and flutes are played by Native American musicians in the Andes. Their haunting music is played at traditional festivals.
La Paz is the world's highest capital city. It stands at about 3.660 m (12,000 ft) above sea level and is ringed by snowcapped peaks. The Spanish founded La Paz in 1548 on the site of an Aymaran village.
Traditional dress is still worn by many of the poorer people in the mountains. The women wear bright skirts and bowler hats.
Antonio Jose de Sucre (1795-1830) helped to end Spanish rule in South America. Sucre, the official capital of Bolivia, is named after the great general. The city, which was founded in 1538, contains Bolivia's supreme court but most government buildings are in La Paz, the actual capital and largest city.
