Venezuela geographic map. Detailed map of Venezuela with a brief description of the country. Venezuela on the world map.
Geographic map of Venezuela. Detailed map of Venezuela with a brief description of the country. Venezuela on the world map.
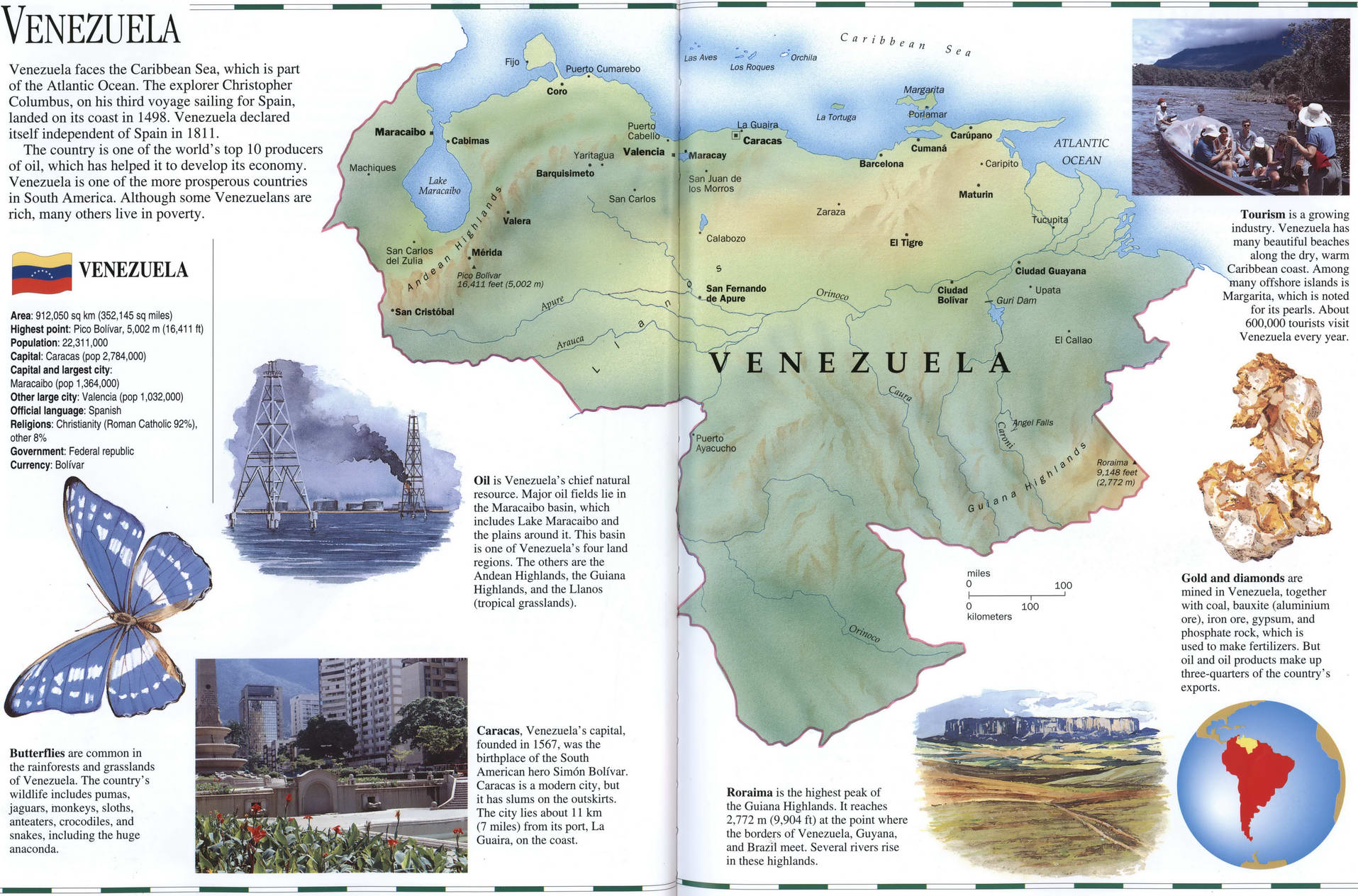
Venezuela geographic description
Venezuela on a map of South America. Detailed geographic map of Venezuela. Full information about Venezuela on one geographical map with cities, rivers, mountains and places of interest.
Venezuela geographic description
Venezuela faces the Caribbean Sea, which is part of the Atlantic Ocean. The explorer Christopher Columbus, on his third voyage sailing for Spain, landed on its coast in 1498. Venezuela declared itself independent of Spain in 1811.
The country is one of the world's top 10 producers of oil, which has helped it to develop its economy. Venezuela is one of the more prosperous countries in South America. Although some Venezuelans are rich, many others live in poverty.
VENEZUELA
Area: 912,050 sq km (352,145 sq miles) Highest point: Pico Bolivar, 5,002 m (16,411 ft) Population: 22,311,000 Capital: Caracas (pop 2,784,000) Capital and largest city: Maracaibo (pop 1,364,000) Other large city: Valencia (pop 1.032,000) Official language: Spanish Religions: Christianity (Roman Catholic 92%), other 8%.
Government: Federal republic Currency: Bolivar is Venezuela's chief natural resource. Major oil fields lie in the Maracaibo basin, which includes Lake Maracaibo and the plains around it. This basin is one of Venezuela's four land regions. The others are the Andean Highlands, the Guiana Highlands, and the Llanos (tropical grasslands).
Butterflies are common in the rainforests and grasslands of Venezuela. The country's wildlife includes pumas, jaguars, monkeys, sloths, anteaters, crocodiles, and snakes, including the huge anaconda.
Caracas, Venezuela's capital, founded in 1567, was the birthplace of the South American hero Sim6n Bolivar. Caracas is a modern city, but it has slums on the outskirts. The city lies about 11 km (7 miles) from its port. La Guaira. on the coast.
Tourism is a growing industry. Venezuela has many beautiful beaches along the dry, warm Caribbean coast. Among nany offshore islands is Margarita, which is noted for its pearls. About 600,000 tourists visit Venezuela every year.
Gold and diamonds are mined in Venezuela, together with coal, bauxite (aluminium ore), iron ore, gypsum, and phosphate rock, which is used to make fertilizers. But oil and oil products make up three-quarters of the country's exports.
Roraima is the highest peak of the Guiana Highlands. It reaches 2.772 m (9,904 ft) at the point where the borders of Venezuela, Guyana, and Brazil meet. Several rivers rise in these highlands.
